Japanese-American Incarceration During World War II
In his speech to Congress, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt declared that the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, was "a date which will live in infamy." The attack launched the United States fully into the two theaters of World War II – Europe and the Pacific. Prior to Pearl Harbor, the United States had been involved in a non-combat role, through the Lend-Lease Program that supplied England, China, Russia, and other anti-fascist countries of Europe with munitions.
The attack on Pearl Harbor also launched a rash of fear about national security, especially on the West Coast. In February 1942, just two months later, President Roosevelt, as commander-in-chief, issued Executive Order 9066 that resulted in the internment of Japanese Americans. The order authorized the Secretary of War and military commanders to evacuate all persons deemed a threat from the West Coast to internment camps, that the government called "relocation centers," further inland. Read more...
Primary Sources
Links go to DocsTeach, the online tool for teaching with documents from the National Archives.
Teaching Activity
Additional Background Information
Prior to the outbreak of World War II, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) had identified German, Italian, and Japanese aliens who were suspected of being potential enemy agents; and they were kept under surveillance. Following the attack at Pearl Harbor, government suspicion arose not only around aliens who came from enemy nations, but around all persons of Japanese descent, whether foreign born (issei) or American citizens (nisei). During congressional committee hearings, representatives of the Department of Justice raised logistical, constitutional, and ethical objections. Regardless, the task was turned over to the U.S. Army as a security matter.
The entire West Coast was deemed a military area and was divided into military zones. Executive Order 9066 authorized military commanders to exclude civilians from military areas. Although the language of the order did not specify any ethnic group, Lieutenant General John L. DeWitt of the Western Defense Command proceeded to announce curfews that included only Japanese Americans. Next, he encouraged voluntary evacuation by Japanese Americans from a limited number of areas; about seven percent of the total Japanese American population in these areas complied.
On March 29, 1942, under the authority of the executive order, DeWitt issued Public Proclamation No. 4, which began the forced evacuation and detention of Japanese-American West Coast residents on a 48-hour notice. Only a few days prior to the proclamation, on March 21, Congress had passed Public Law 503, which made violation of Executive Order 9066 a misdemeanor punishable by up to one year in prison and a $5,000 fine.
Because of the perception of "public danger," all Japanese Americans within varied distances from the Pacific coast were targeted. Unless they were able to dispose of or make arrangements for care of their property within a few days, their homes, farms, businesses, and most of their private belongings were lost forever.
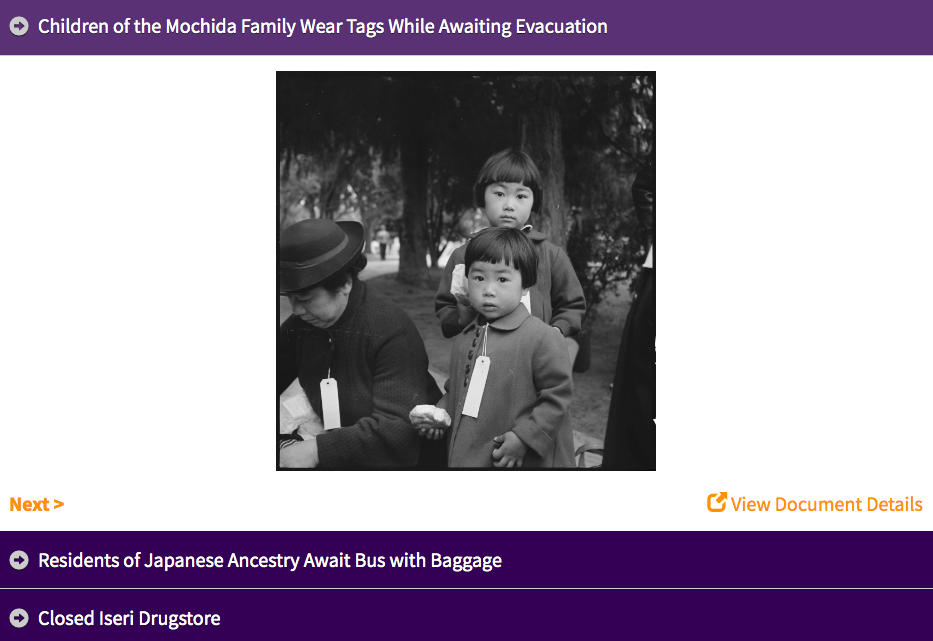
From the end of March to August, approximately 112,000 persons were sent to "assembly centers" – often racetracks or fairgrounds – where they waited and were tagged to indicate the location of a long-term "relocation center" that would be their home for the rest of the war. Nearly 70,000 of the evacuees were American citizens. There were no charges of disloyalty against any of these citizens, nor was there any vehicle by which they could appeal their loss of property and personal liberty.
"Relocation centers" were situated many miles inland, often in remote and desolate locales. Sites included Tule Lake and Manzanar in California; Gila River and Poston in Arizona; Jerome and Rohwer in Arkansas, Minidoka in Idaho; Topaz in Utah; Heart Mountain in Wyoming; and Granada in Colorado. (Incarceration rates were significantly lower in the territory of Hawaii, where Japanese Americans made up over one-third of the population and their labor was needed to sustain the economy. However, martial law had been declared in Hawaii immediately following the Pearl Harbor attack, and the Army issued hundreds of military orders, some applicable only to persons of Japanese ancestry.)
In the "relocation centers" (also called "internment camps"), four or five families, with their sparse collections of clothing and possessions, shared tar-papered army-style barracks. Most lived in these conditions for nearly three years or more until the end of the war. Gradually some insulation was added to the barracks and lightweight partitions were added to make them a little more comfortable and somewhat private. Life took on some familiar routines of socializing and school. However, eating in common facilities, using shared restrooms, and having limited opportunities for work interrupted other social and cultural patterns. Persons who resisted were sent to a special camp at Tule Lake, CA, where dissidents were housed.
In 1943 and 1944, the government assembled a combat unit of Japanese Americans for the European theater. It became the 442d Regimental Combat Team and gained fame as the most highly decorated of World War II. Their military record bespoke their patriotism.
As the war drew to a close, "internment camps" were slowly evacuated. While some persons of Japanese ancestry returned to their hometowns, others sought new surroundings. For example, the Japanese-American community of Tacoma, WA, had been sent to three different centers; only 30 percent returned to Tacoma after the war. Japanese Americans from Fresno had gone to Manzanar; 80 percent returned to their hometown.
The internment of Japanese Americans during World War II sparked constitutional and political debate. During this period, three Japanese-American citizens challenged the constitutionality of the forced relocation and curfew orders through legal actions: Gordon Hirabayashi, Fred Korematsu, and Mitsuye Endo. Hirabayashi and Korematsu received negative judgments; but Mitsuye Endo, after a lengthy battle through lesser courts, was determined to be "loyal" and allowed to leave the Topaz, Utah, facility.
Justice Murphy of the Supreme Court expressed the following opinion in Ex parte Mitsuye Endo:
I join in the opinion of the Court, but I am of the view that detention in Relocation Centers of persons of Japanese ancestry regardless of loyalty is not only unauthorized by Congress or the Executive but is another example of the unconstitutional resort to racism inherent in the entire evacuation program. As stated more fully in my dissenting opinion in Fred Toyosaburo Korematsu v. United States, 323 U.S. 214 , 65 S.Ct. 193, racial discrimination of this nature bears no reasonable relation to military necessity and is utterly foreign to the ideals and traditions of the American people.
In 1988, Congress passed, and President Reagan signed, Public Law 100-383 – the Civil Liberties Act of 1988 – that acknowledged the injustice of "internment," apologized for it, and provided a $20,000 cash payment to each person who was incarcerated.
One of the most stunning ironies in this episode of denied civil liberties was articulated by an internee who, when told that Japanese Americans were put in those camps for their own protection, countered "If we were put there for our protection, why were the guns at the guard towers pointed inward, instead of outward?"
A note on terminology: The historical primary source documents included on this page reflect the terminology that the government used at the time, such as alien, evacuation, relocation, relocation centers, internment, and Japanese (as opposed to Japanese American).
 Materials created by the National Archives and Records Administration are in the public domain.
Materials created by the National Archives and Records Administration are in the public domain.