
18th Annual Preservation Conference
Preservation Reformatting—
Use, Sustainability and Affordability
Stephen Chapman
Weissman Preservation Center
Harvard University Library
March 27, 2003
Harvard Practices:
Multiple Technologies and Services
- Film
- 35mm microfilm, film negatives, slides, photographic prints
- Digital
- b/w, grayscale, color images; full text (OCR); metadata
- Hybrid (microfilm + digital) (film/print surrogate + digital)
- text: 35mm microfilm, 1-bit digital images (and OCR)
- pictorial: film or print surrogate, 24-bit digital images
- Hybrid (microfilm + digital) + Direct Digital
- 35mm microfilm and 1-bit (b/w) digital images: all pages,
+ grayscale or color (direct) digital images: selected pages
- 35mm microfilm and 1-bit (b/w) digital images: all pages,
Preservation & Access Mission
Perpetuate use.
“Preservation … shall not come at the expense of usability.”
… goal is to perpetuate access to that portion of source materials identified
as essential to continued usefulness for stated purposes.
Weissman Preservation Center
Reformatting Infrastructure:
Time Capsule
To preserve information content...
- Production
- Make copies
- Acquisition
- Move copies from production to storage
- Storage
- Maintain copies and environments
Reformatting Infrastructure:
[No] Time Capsule
To preserve information content...
- Production
- Make copies
- Acquisition
- Move copies from production to storage
- Storage
- Maintain copies and environments
Reformatting Infrastructure:
Library
To preserve use of information content...
- Production
- Acquisition
- Storage
- Discovery
- Catalogs
- Delivery
- Reader/printers, slide projectors, networked PCs
Two Contexts of Usability
- Usable by machines
- film duplicators, enlargers, reader/printers
- image processing software, web browsers
- Usable by people
- preservation managers and technical specialists
- scholars and other users
Analog, Digital or Hybrid?
Users and use requirements
- Owner, to manage risk of loss
- copy mss for preservation backup, not distribution
- Librarian, to build collection
- 491 reels duped in FY02, including 63 titles by NLM to fill gaps
- Users, to “access” and “study” item(s)
- definitions dictate delivery format
Affordability: Pragmatic Solutions
- Production
- Acquisition and storage
- Discovery
- Delivery
- Standards and quality metrics
- Centralized repositories
- Scalable delivery services that meet user needs
- Maximum intervals between interventions
- When obsolete, you must repeat (reformatting).
- Considered uses of production technology(ies)
- Masters
- Deliverables
Obsolescence
- Industry-created
- Product discontinuation (mfrg and/or support)
- Example: KODAK EKTAPAN Film
- Example: color-matched printing from transparency film
- User-created
- Change in expectation: abandonment of format (service model) or device
- Example: shift from reserves (photocopies) to e-reserves (digital) to distribute course materials
- Example: shift from PCs to PDAs
- Product discontinuation (mfrg and/or support)
Role of Analog or Digital
Meet requirements for production, storage and delivery in most affordable way
- Production
- Once-per-? costs for masters: optimize for automated production of range of deliverables
- Periodic costs for delivery
- Storage
- Annual costs, regardless of use
- Delivery
- Costs largely determined by market factors: users/user needs, availability of technology
Harvard Infrastructure
Imaging Equipment Photographs
1
| 2
| 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
Digital Repository Service Web Page
Harvard Libraries: Other Catalogs Web Page
Harvard University Library Office for Information Services
Infrastructure Systems and Services Diagram
Harvard Products
Product Specifications Tailored to Project
- Formats and versions
- Analog and digital
- Standards, best practices, funding & repository policies
- Required output(s) [for use] in near-term
- Analog and digital
- Technical specifications and quality control
- Analog
- Conventions for “preservation”: standards, best practices, funding policies, quality requirements
- Digital
- No conventions for “preservation”: informed by extent of vendor services, empirical review of samples, price
- Analog
Production Strategies: Text
- Filming of bound and unbound materials
- Use requirements satisfied with analog copies
- Filming of bound volumes: scanning of film
- Retain bindings, 1-bit output, direct bound scanning not yet viable for high production
- Direct digitization of print
- 8-bit, 24-bit output
- Autofeed scanning of brittle pages (or photocopies)
- Multiples, 1-bit output, film quality not uniform
- Legacy microfilm scanning -- exploring
- Depends upon quality of film
Production Strategies: Photographs
- Direct digitization of prints, film, plates
- HUAM exclusively digital
- Photographic services
- Film masters
- Darkroom (chemical) b/w prints
- Digitization of legacy film
- Post processing varies according to budget
- File sizes range from 15-200 MB for color work…
Scanned Transparency Sample Image
Harvard Prices
repository storage, (some) delivery
Repository Storage Annual Charges, by Size
- Harvard Depository
- $3.91 per Billable Square Foot (standard)
- $9.85 per Billable Square Foot (film vault)
- Harvard Digital Repository Service
- $5.00 per GB (1,024 MB)
Text Storage (Masters):
Harvard Repository Costs Compared
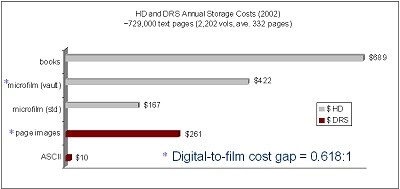
Scanned Images of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's Hyperion
Text Storage (Masters):
Harvard Repository Costs Compared
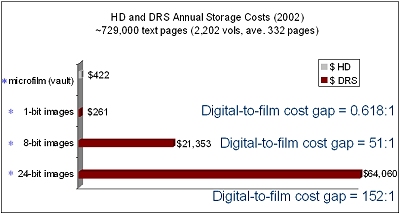
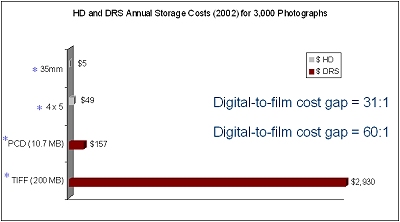
Photographs Storage (Masters):
Harvard Repository Costs Compared
Delivery Services: Newspapers
Analog, Digital or Both?
Cost
- Production + storage + discovery + delivery
- Factoring use requirements
- Factoring volume
- Factoring infrastructure
- Factoring business models
- Factoring time (between interventions)
Thank you
Stephen Chapman
Preservation Librarian for Digital Initiatives
Weissman Preservation Center
stephen_chapman@harvard.edu
http://preserve.harvard.edu/services/
http://hul.harvard.edu/ois/
http://hul.harvard.edu/hd/
http://hul.harvard.edu/ois/systems/drs/
http://hul.harvard.edu/ldi/
http://jodi.ecs.soton.ac.uk/
Preservation Conference 2003 Main Page



